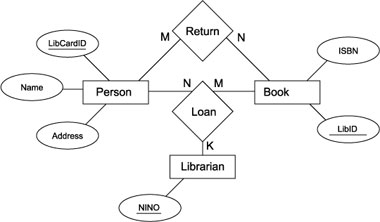
1.4. ER diagrams
In this lecture we look at...
[Section notes PDF 75Kb].
1.4.01. ER Diagrams and Relational mapping
- Design communication techniques
- ER diagrams
- ER to relational mapping
- Entities to Objects
- Type Inheritance
- EER diagrams
- UML
- Web DB Integration
1.4.03. Design in the modern context
- Team based development
- Documentation
- Value of design over description
- DB sketching (left hand side)
- Concept more important than perfection
- Design iteration
- Mini-world as approximation
- Categorisation to create entities
- Verb’ing to create actions/relationships
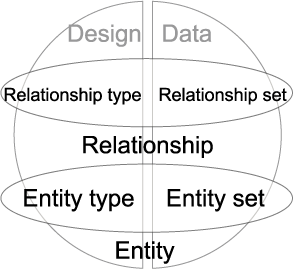
1.4.04. Database Left:right divide
- Design
- Catalog, Meta-data, Intension, or Database schema
- Entity type
- Relationship type
- State
- Set of occurences/instances, Extension, snapshot
- Entity set
- Relationship set
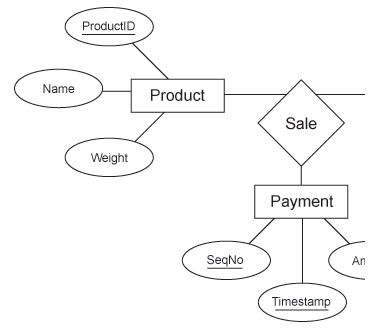
1.4.05. Basic ER diagram
- Typically part of a system
- (Strong) Entities
- Product
- Customer
- Payment
- Relationships
- Sale
1.4.06. Mapping ER to Relation DB tables
- Intuitive mapping
- Entities as tables
- Attributes as columns
- Relationships are more difficult
- Key sharing mechanism
- Foreign key references primary key
- Where to put the foreign key forms the intuitive guide to the rest of
the mapping
1.4.07. ER to Relational mapping
- Step-by-step approach
- Strong entities
- Create relation including (simplified) attributes
- Weak entities
- Create relation inc. attr, foreign/pri key of owner
- Binary relationship S:T, 1:1
- Choose relation, say S (with total participation) and inc. foreign/pri
key of T - inc. relationship attributes
1.4.08. Cardinality
- Specifies number of relationship instances a single entity can participate in
- S:T (1:1)
- An entity from table S can is related to one, and only one entity from table T
- 1:1, 1:N, N:M
- DEPARTMENT : EMPLOYEE
- EMPLOYEE : EMPLOYEE
- PROJECT : EMPLOYEE
1.4.09. ER to Relational mapping
- Binary relationship 1:N
- Choose relation T (N-side) inc. foreign/pri key of S
- Binary relationship M:N
- Create relation, inc. foreign/pri keys of S&T
- Multivalued
- For each mv_attr, create new relation, inc. foreign/pri key of parent
- n-ary relationship
- Create new relation, inc. all foreign/pri keys of participating
entities
1.4.10. Participation
- Participation constraints
- Existence of an entity dependant upon
- being related to another entity
- via relationship type (left hand/design)
- Total (")/Existence
dependency (double line) - Every student must be in a faculty
- For every entity in the total set of students
- Partial ($) (single line)
- Some students are student_representatives
- There exists some entity(s) within the set of all…