1.3. Joins
In this lecture we look at...
[Section notes PDF 233Kb].
1.3.01. Introduction
- Recap: pulling data out of individual relations
- By row, by column
- Select and project
- Access across multiple relations
- Miniworld approximation
- Fragmenting entities by cardinality
- Tuples as entity fragments
- Relationships within relations
- Joins
- Join types (condition and unmatched)
1.3.02. Access across relations
- Relational model allows multiple relations to exist within one database schema
- Relations can be accessed individually or together (joins).
- Referential integrity
- Relations relating
- Pulling data out of single relations
- Select and project
- Pulling related data out of
- Multiple relations using Join
1.3.03. Miniworld approximation
- Universe of Discourse, or Miniworld
- Miniworld is an incomplete model of the real world
- The relational data model as a model for the miniworld
- Approximation
- Separate and distinct entities
- Single complex entities
- Separate related entities
- Cardinality of relationships
- Each relation made up of attributes
- Values can be used as references
1.3.04. Pointing mechanism
- Relation has a Primary key
- Tuple contains Primary key value
- Foreign keys
- Tuples can contain a reference to another relation's Primary key
- Just numbers
One number identifies a single tuple in one relation (local), one number identifies a single tuple in another relation (foreign).
1.3.04b. Pointing mechanism example in C
- C programming language
- Memory addresses, or pointers
int a=0; int b=0; a = &b;
- a points to b
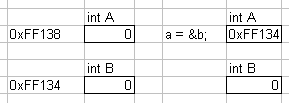
In databases, typically done with unique identifiers (IDs) rather than memory addresses.
1.3.04c. Pointing mechanism with structures
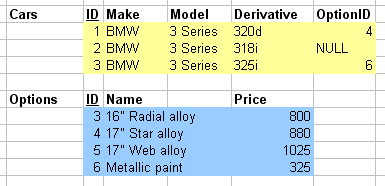
- Foreign key importing
typedef struct car { int ID; char[] make; char[] model; char[] derivative; int optionID; } car; typedef struct option { int ID; char[] name; int price; } option; car c; option o; //...data structure populating c.optionID = o.ID;
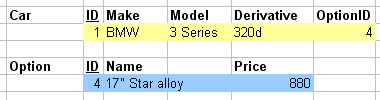
1.3.05. Relational cardinality
- 1:0 relationships
- Single entity
- Uniquely indentifiable
- Candidate keys
- Primary Key
- 1:1 relationships
- Two entities, A and B
- 1 A relates to 1 B and vice versa
- 1:N relationships
- M:N relationships
1.3.06. Relationships in the relational model
- Two relations, A and B
- A side, B side, 1 side, N side
- 1:1 relationships
- Key can go on either side
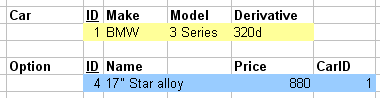
- 1:N relationships
- Key cannot go on 1 side
- Has to go on N side

- M:N relationships
- Nowhere obvious for the key to go
- Create new pairing relation
1.3.07. Joins
- Phase change, different point in lifecycle
- Join operation
- Combines related tuples, conditionally
- From two relations
- Into single tuples
- Allows processing of relationships
- Among multiple relations
1.3.08. Joins, canonical algebraic form
- Conditional (on join condition)
- Only combines tuples where true
- Cartesian product (conditionless)
- example of conditionless join
- all tuples combined
- R ⋈true S
- ⋈, Binary operator
e.g. R ⋈<join_condition> S
1.3.09. Join equivalence
- Equivalent to sequence
- Cartesian product (X)
- followed by Selection (s)
- ACTUAL_DEPENDENTS =
sSSN=ESSN(EMPNAMES X DEPENDENT) - or
- ACTUAL_DEPENDENTS =
EMPNAMES ⋈ SSN=ESSN(DEPENDENT)
1.3.10. Join types (condition)
- Theta: Ai q Bj
(A from R, B from S) - q is comparison operator
=,<,>,!=,>= - Ai and Bj share the same domain
- Equi: Ai = Bj
- Theta join where q is =
- Natural: Ai and Bj are the same attribute
- in two separate relations (name and domain)
- * denotes natural join
- e.g. EMPNAMES * DEPENDENTS
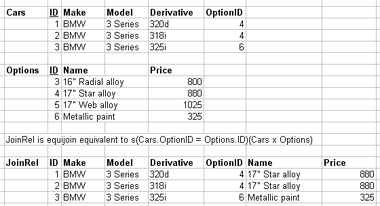
1.3.11. Join types (inner and outer)
- Inner joins
- not the only joins
- eliminate tuples without a matching counterpart
- i.e. tuples with a null value for the join attribute are discarded
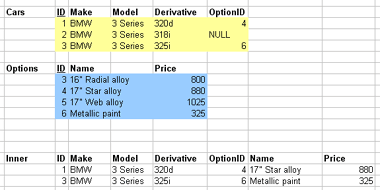
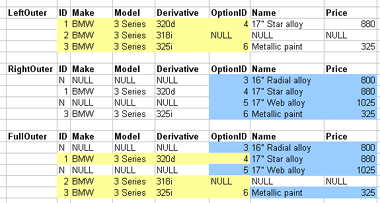
1.3.12. Outer joins
- Outer joins control what's discarded
- Keep unmatched tuples in either
- Left, right, or both relations
- Left, right of full outer join correspondingly