5.2. Decision Support
In this lecture we look at...
[Section notes PDF 85Kb]
5.2.01. Introduction
- Decision support systems (DSS)
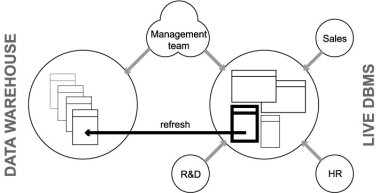
- Duplicates of live systems, historical archiving
- Primarily read-only
- Load and refresh operations
- Integrity
- Assumptions about initial data
- Large, indexed, redundancy
5.2.02. DSS Management
- Design
- Logical
- Temporal keys, required to distinquish historical data (since:to
current & during:within interval) - Physical (Hash indexes, Bitmap indexes)
- Controlled Redundancy
- Synchronisation/update propogation
- Synchronous (update driven)
- Asynchronous (query driven)
5.2.03. Data Preparation
- Extract
- pulling from live database system(s)
- Cleansing
- Transformation and Consolidation
- migrating from live or legacy system design
to DSS design - Load (DSS live/query-able)
- Refresh (latest update)
5.2.04. Querying
- Boolean expression complexity
- heavy WHERE clauses
- Join complexity
- Normalised databases, many tables
- Facts distributed across tables
- Joins required to answer complex questions
- Function and Analytic complexity
- Often require non-DBMS functions
- Smaller queries with interleaved code
5.2.05. Data Warehouse
- Specific example of DSS
- Subject-orientated
- e.g. customers/products
- Non-volatile
- once inserted, items cannot be updated
- Time variant
- Temporal keys
- Accuracy and granularity issues
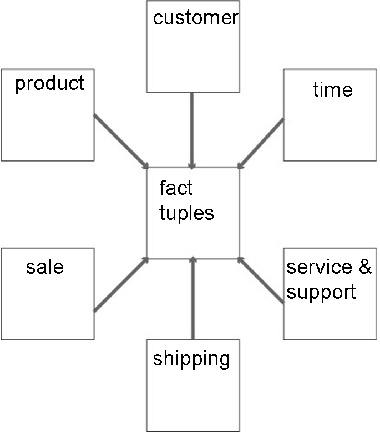
5.2.07. Dimensional Schema
- Consider product, customer, sales data
- Each sale represents a specific event
- when a product was purchased
- when a customer bought something
- when a sale was recorded
- Each can be thought of as an axis
or dimension (3D) - Each occurred at a moment in time (4D)
5.2.08. Star schemae and Hypercubes
5.2.09. Hypercubes
- Hypercube is also a multi-processor topology inspired by a 4D shape
- Used by Intel’s iPSC/2
- Good at certain database operations
- e.g. Duplicate removal
- MIMD